Electric heat pumps: The safe, affordable, efficient choice
If you are in the market for a new heating system or looking to upgrade your existing system, make sure you take a look at electric heat pumps. Heat pumps–air source and geothermal–are the most reliable and energy efficient way to heat and cool your home. Below are frequently asked questions about air source heat pumps to help members evaluate the pros and cons for your home or business.
Q: Why would you heat a home or business with electricity?
A: Today’s electric heating equipment is efficient and competitive with other fuel sources. Electric heat is clean, consistent and safe.
Q: Can an electric heat pump save you money?
A: Yes, if you are building new construction or replacing a furnace, I recommend researching an electric heat pump. An ENERGYSTAR-certified heat pump provides highly efficient heating and cooling. Replacing or adding a system that both heats and cools is an all-in-one solution that can help reduce your energy bills.
An air source heat pump is 150 to 300% efficient. A geothermal heat pump is 400% efficient, and can even go higher.
Here's a simple cost comparison:
If you have a high-efficiency propane furnace, you'd have to purchase LP at $1.05/gallon or less to compete with an air source heat pump on Polk-Burnett's winter electric rate (Dec. 2021).
Q: How does an AIR SOURCE heat pump work?
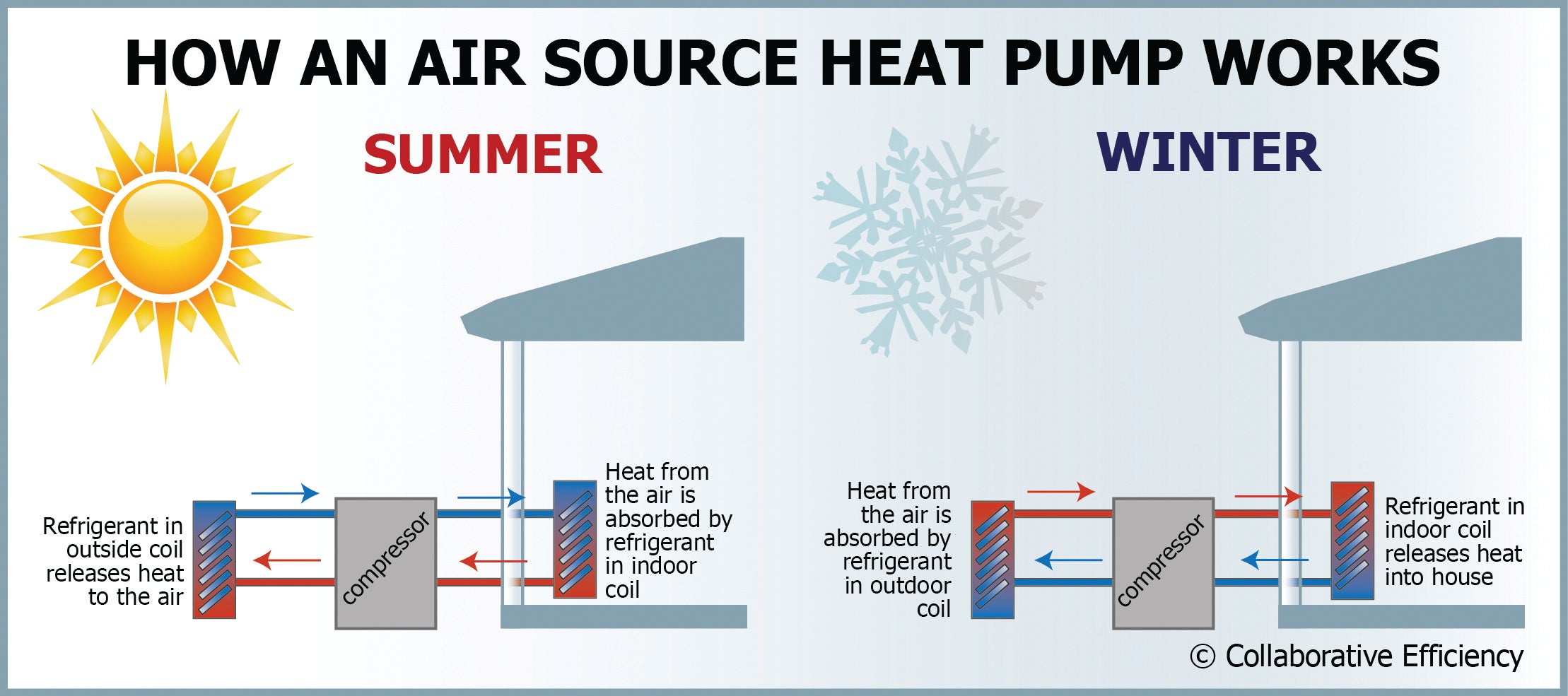
A: Heat pumps capture the heat that naturally occurs in the air or ground. Like your refrigerator, heat pumps use electricity to move heat, making your home cooler in the summer and warmer in the winter.
In summer, an air source heat pump acts as an air conditioner that draws heat from your home’s air and transfers it outside. In winter, the direction is reversed. The system transfers heat from the outside air into your home, using a liquid refrigerant and evaporation through coils (see chart below).
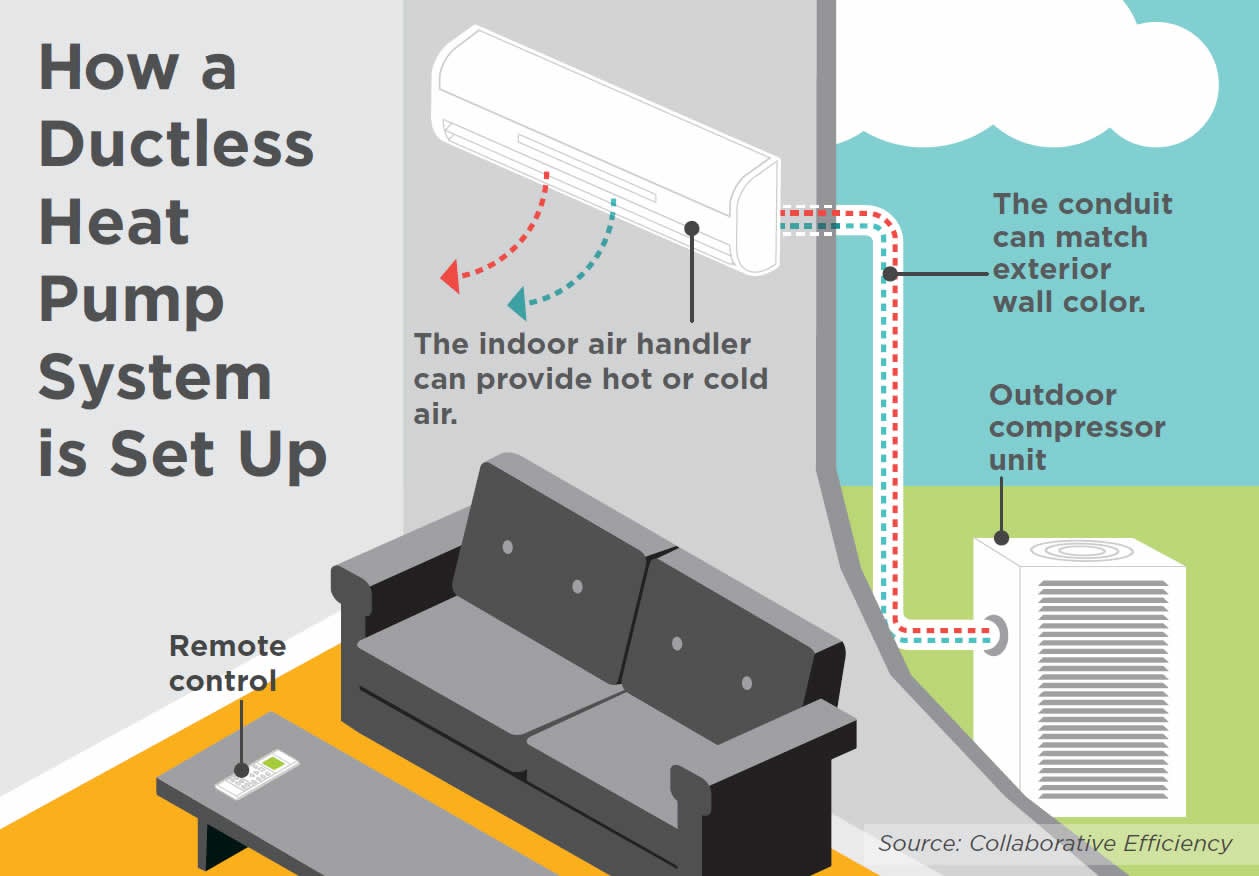
A heat pump has two major components: the condenser, also called a compressor, circulates refrigerant through a system of copper or aluminum coils; and an air handler, which distributes the conditioned air. Most heat pumps are split systems, with the condenser outside and the air handler inside.
Q: Do air source heat pumps work in extremely cold weather?
A: The best time of year for an air source heat pump is during shoulder months: March, April and May in the spring and September, October and November in the fall. Air source heat pumps may need alternate heat for extremely cold days.
As the outside temperature drops, the efficiency of air source heat pumps and the delivery air temperature also drop. The most common air source heat pumps operate efficiently down to 10 to 20 degrees. With advances in technology, some heat pumps can now operate well below zero, while maintaining efficiency and comfort.
We offer rebates to help members make the switch to energy efficient heat pumps.
Tax credits may also be available.
Give us a call, 800-421-0283, ext. 595. We can help you compare heating and cooling options.
We also recommend you work with a certified HVAC contractor and your tax adviser.
Also read about geothermal heat pumps.